AI Readiness in the Pharmaceutical Industry
This report aims to determine the capacity of pharmaceutical companies to adopt and adapt AI technologies to their activities. In sum, AI readiness is just that: what processes and tools have leading industry players implemented to prepare for this technological change? At Pugatch Consilium, we studied a series of factors revelatory of AI readiness, which can be broken down into 3 stages.
Transparency is key when it comes to AI. It ensures accountability of pharma companies, better acceptance by the general public, patient safety, and possible regulatory and legal compliance. We tried to incorporate this aspect into our Index, by basing our analysis on public sources of information only. These include patent databases, social media posts, press interviews, official statements, corporate documents and reports, corporate websites, and media articles.
All data that serves as the basis of our analysis was collected until October 2024; this is prone to change, and any posterior evolution of these factors is not reflected in the report.
2019 Biopharmaceutical Competitiveness & Investment (BCI) Survey
Emerging Markets
In the global competition for biopharmaceutical investment policy environments either enable or hinder an economy’s capacity to compete. Today who is winning this race and who is trailing? What aspects of individual economies’ environments are providing momentum and what is holding them back? And ultimately, how can governments improve their competitiveness and secure a larger piece of global biomedical investment?
To answer these questions we turned to biopharmaceutical country executives, who are at the forefront of understanding how different aspects of the local policy environment factor in when discussing whether to allocate further resources in the economy. The 2019 Emerging Markets Biotechnology Competitiveness and Investment (BCI) Survey is a global executive opinion survey and index of the biomedical investment attractiveness in 17 fast-growing emerging markets in the world.

Annex
Just as for previous editions this report is accompanied by an Annex. This Annex is a detailed account of biotech policy inputs and outputs for each economy.
Building the Bioeconomy 6th Edition
Pugatch Consilium is today releasing the sixth edition of the Building the Bioeconomy, a series of papers commissioned by the Biotechnology Industry Organization
This year’s edition adds to the analysis eleven countries, further increasing the geographic and economic diversity of the countries sampled. Yet, the findings of the report reach beyond the 44 economies covered. Any country who is willing to reap the economic and social benefits of biotechnologies can find in the Building the Bioeconomy some relevant guidelines on how to go about building thriving biotechnology sectors.
Benchmarking Success
Evaluating the Orphan Regulation and its impact on patients and rare disease R&D in the European Union
Pugatch Consilium is today releasing a new study – Benchmarking Success: Evaluating the Orphan Regulation and its impact on patients and rare disease R&D in the European Union.
Within the context of the European Commission’s Evaluation of the legislation on medicines for children and rare diseases, the study examines whether the EU Orphan Regulation has accomplished its aim of incentivising the development and introduction of new therapies for rare diseases onto the EU market, and explores some of the current and future challenges and questions about new product development for rare diseases. This includes questions such as:
– How to ensure real patient access to new medicines following market authorisation?
– How to further incentivise the development of orphan medicines for paediatric use?
– And how to continue to provide effective incentives through defined market exclusivity periods?
On whether or not the Orphan Regulation has achieved its stated objectives the evidence is quite clear: Since its introduction, over 150 orphan medicinal products have been approved by the EMA for over 90 rare diseases, and the EU is spearheading global clinical research on rare diseases, with some 2,000 clinical trials providing early access to potential novel treatments for thousands of EU patients with rare diseases each year.
Building the Bioeconomy 5th Edition
National Biotechnology Industry Development Strategies Globally
A Pugatch Consilium study released today commissioned by the Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO) highlights strategies, policies and best practices that have been successful in creating an environment in which biotechnology innovation can flourish around the world.
The fifth edition of the Building the Bioeconomy report shows the correlation between economies with pro-innovation policy frameworks and those achieving strong biotechnology outputs. By examining 28 different indicators ranging from public policy inputs to biotechnology outputs, the report provides a full and detailed analysis of the biotechnology environment for 33 countries from all major regions of the world.
This data-driven report developed in partnership by Pugatch Consilium and BIO, compares economies on over 20 policy inputs and biotech outputs showing how regulations effect success or failure in driving industry growth. Economies that have stronger environments with all enabling policy factors in place yield higher biotechnology outputs. Adopting a strong policy framework is key to reaping the economic and social benefit of this important industry.
Why IP Incentives Matter for Life Sciences Innovation – In Europe and Beyond
How IP incentives spur biopharmaceutical innovation and the creation of new health technologies
Pugatch Consilium is today releasing a new report – A Critical Incentive – Not a Barrier! How IP incentives spur biopharmaceutical innovation and the creation of new health technologies.
This analysis could not be more timely. In Europe, for example, the EU Commission is seriously considering ways to weaken the intellectual property protections that support hundreds of thousands of life sciences jobs and drive discovery of new treatments and cures for patients.
As the Commission continues its “incentives review”, it must recognize the historical record: IP protections and targeted incentives have stimulated (and continue to stimulate!) new research and the creation and development of new medical products and technologies.
As the global population ages – in part due to medical and pharmaceutical advances – one growing challenge we face is the burden of neurodegenerative diseases. Alzheimer’s and neurodegenerative diseases are a growing disease challenge to not only the patients and families faced with this disease but also the health systems charged with caring for them. Yet despite this growing disease burden the available treatment options for Alzheimer’s and other dementias are limited.
As A Critical Incentive shows there is a blueprint in place to addressing the challenge of Alzheimer’s and other complex disease areas. Instead of weakening IP incentives for medical innovation, a more constructive path would be to think about creating similar incentives for research into Alzheimer’s disease and other disease areas in which there has so far been limited success.
IP incentives are not part of the problem, but part of the solution.
BCI 2017 Latin America Special Report
An executive opinion survey of business leaders and local general managers from the biopharmaceutical industry about the investment environment in 31 markets
Pugatch Consilium has released the 2017 Biopharmaceutical Competitiveness & Investment (BCI) Latin America Special Report. This Report is derived from the main 2017 BCI Survey, a global executive opinion survey and index that measures the relative attractiveness of economies to investment from biopharmaceutical research-based companies.
The Report deep-dives into ten Latin American countries: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Mexico, Panama and Peru. A statistical analysis benchmarks each country in relation to others in the region, revealing their relative attractiveness for biopharmaceutical investment.
Two fundamental findings of the 2017 BCI LatAm Special Report stand out: 1) Focusing on a handful of areas of reform does not lead to a thriving biopharmaceutical sector; instead a holistic comprehensive approach is required addressing variables of the entire biopharmaceutical ecosystem. 2) Achieving and maintaining a successful healthcare system is not guaranteed by brute economic force or market size. Instead, countries need to adopt a “work-in-progress” approach focusing on getting the policies right, and making themselves attractive and competitive. They need to resist tempestuous budget cuts and keep laser-focused on a long-term vision of becoming magnets of biopharmaceutical activity.
This Special Report reveals important insights regarding the impact of biopharmaceutical policies on investment decisions in the challenging and evolving microcosm of Latin America. The report is aimed at supporting policy makers, business executives and other key stakeholders in identifying what economic and policy aspects are hindering the ability to meet today’s healthcare challenges in the region and create a thriving biopharmaceutical sector there.
Debunking the IP and Access to Medicines Myth Once and For All
This report examines a common misperception in the international community: that patents and IP incentives block access to medicines
Pugatch Consilium is releasing the report Unlocking Global Health Strengthening Availability of Essential Medicines by Enhancing Healthcare Financing and Reducing Supply Chain Costs.
Discussions over the impact – positive or negative; rarely neutral – that IP rights have had and continue to have on the creation and dissemination of new ideas and commercial products is as emotional as it is part of economic and social history. This is particularly the case for medical and biopharmaceutical innovation where IP incentives are frequently lambasted. At heart of much of this criticism is a deep skepticism of the value that IP rights bring to biopharmaceutical innovation.
One of the standing arguments made is that IP rights limit access to medical products and technologies in lower and middle income countries.
But is this true?
One area which is frequently overlooked within this debate is the issue of access to essential medicines, the majority of which are actually off-patent.
BCI 2017 Report and Results
An executive opinion survey of business leaders and local general managers from the biopharmaceutical industry about the investment environment in 31 markets
Pugatch Consilium has released the 2017 Biopharmaceutical Competitiveness & Investment (BCI) Survey. An executive opinion survey, in 2017 the BCI polled business leaders and local general managers from the biopharmaceutical industry about the investment environment in 31 markets.
The headline results of the 2017 BCI Survey include:
• The policy environment matters a great deal for biopharmaceutical investment decisions. Economies with policies supporting biopharmaceutical innovation and investment are much more likely to actually secure investment compared to economies employing policies that are viewed as drawbacks. The 2017 BCI scores are positively linked to the rate of clinical trial activity (as one proxy for biopharmaceutical investment).
• In terms of newcomer markets, those rated as less likely to secure investment in the BCI and exhibiting relatively low levels of clinical research – including the BRICs and many APAC countries – are ones displaying significant challenges in the areas of market access, intellectual property protection and localization requirements. The share of economies where these areas were identified as top barriers to investment rose by 50% in 2017 compared to the 2016 BCI.
• At the same time, many of these economies demonstrated year-on-year improvements in R&D and clinical trial capacity in 2017, suggesting real potential for biopharmaceutical innovation and investment if stronger policy fundamentals were in place.
• For mature markets, the BCI results point to market access and regulatory delays as the weakest links among those economies rated less likely to secure investment. Cost containment measures, discrimination against IP owners and other policies that jettison support for innovation are top of mind for innovators making decisions about where to invest.
For each individual market, the BCI report also provides a detailed breakdown of the market’s results, with a special focus in 2017 on which policy trends are most detrimental or supportive of biopharmaceutical investment.
Unintended Consequences
A study on the negative economic consequences of an SPC export exemption in Europe
The study (which is also available via the Social Science Research Network, SSRN) models the economic impact an SPC manufacturing and export exemption would have on the European and global research-based biopharmaceutical industry.
In October 2015 the European Commission released its report Upgrading the Single Market: more opportunities for people and business, which details the overarching initiative to reform and deepen the single market with the purpose of spurring economic growth, job creation and reducing administrative burdens. As part of this review the Commission announced its intentions to explore options for recalibrating certain elements of SPC protection. One such option put forth by the Commission is to provide European manufacturers of generic drugs and biosimilars with an SPC manufacturing exemption.
Our study finds that implementation of an EU wide SPC manufacturing and export exemption would potentially result in annual losses ranging between USD2.675 billion and up to USD5.35 billion to the global innovative biopharmaceutical industry, with approximately USD1.34 billion to USD2.27 billion of these attributed to the European innovative biopharmaceutical industry.
Translating these losses to current levels of biopharmaceutical sector employment and R&D investment the effect of the introduction of an EU wide SPC manufacturing and export exemption could be between 4,500-7,700 direct job losses (with an additional 19,000-32,000 indirect job losses) and a decrease of between EUR215 million to EUR364 million in R&D investment.
Building the Bioeconomy 4th Edition
National Biotechnology Industry Development Strategies Globally
A new study by international research consultancy Pugatch Consilium (commissioned by the Biotechnology Industry Organization) examines those national innovation strategies, policies and best practices that have been successful in creating an environment in which biotechnologies and biotechnological innovation can flourish.
2017 marks the fourth edition of the Building the Bioeconomy series of papers examining national biotechnology industrial policies. This year’s edition includes 26 countries from all major regions of the world. Examining 28 different indicators ranging from public policy inputs to biotechnology outputs that together provide a full and detailed measure of the complete biotechnology environment for all countries included, the study finds that economies that have the right policy framework and create positive, incentive based environments tend to be the most successful in achieving strong biotechnology outputs.

Annex
Just as for previous editions this report is accompanied by an Annex. this Clinical Trials Policy Annex is a briefing document on the clinical research policy environment.
Challenges and Opportunities – Developing the Biotechnology Sector in Colombia
New Pugatch Consilium report finds Colombia could see over 100 new clinical trials and up over $450 million in economic gains per year with policy reform
The purpose of this report is to, firstly, give a comparative overview of the biotechnology sector in Colombia and, secondly, provide an estimate of how an improvement to Colombia’s policy environment can result in higher biotechnology outputs including rates of biomedical FDI and clinical trials.
The report maps the current policy environment as it relates to biotechnology in Colombia and gives a detailed comparison on key major biotechnology and R&D related outputs between Colombia and other economies.
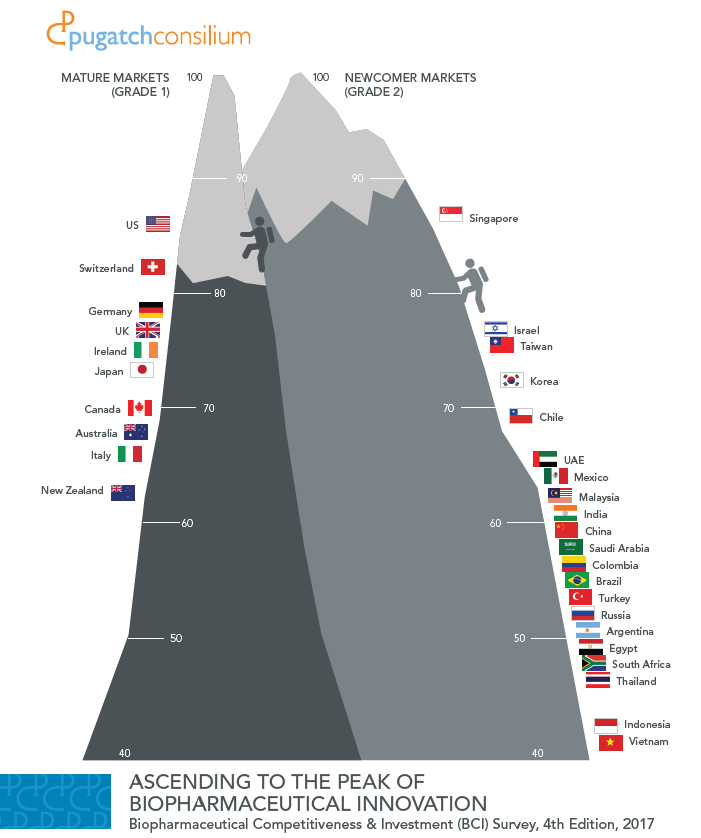
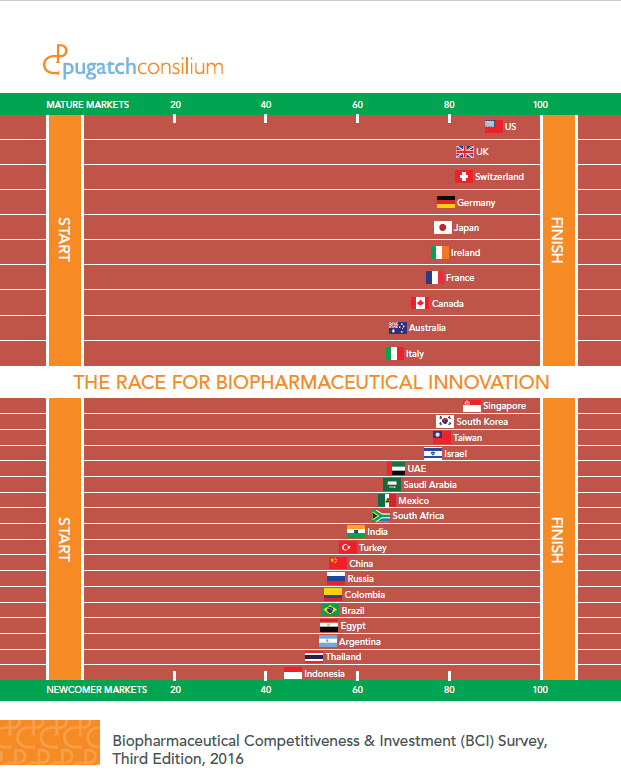
BCI 2016: The Race for Biopharmaceutical Innovation
Pugatch Consilium has launched the third edition of the Biopharmaceutical Competitiveness & Investment (BCI) Survey: The Race for Biopharmaceutical Innovation
A global executive opinion survey and index of economies’ attractiveness for biomedical investment, in 2016 the BCI covers 28 strategic markets and gauges individual markets in relation to others with similar levels of development. The study was released in Washington DC and Ottawa, Canada, with other local and regional launches to take place throughout the remainder of the year
Annex
Just as for previous editions of Building the Bioeconomy this report is accompanied by an Annex. This Annex contains a detailed discussion of each enabling factor included in this report for each of the sampled economies. It is a reference tool and can be read in conjunction with the main report.
Building the Bioeconomy – 2016
Pugatch Consilium releases new edition of Building the Bioeconomy – Shows how economies that are successful in building a high-tech biotechnology capacity put the right enabling policies in place
Commissioned by the Biotechnology Industry Organization and authored by Pugatch Consilium this series of reports seek to provide an overview of those national innovation strategies, policies and best practices that have been successful in creating an environment in which biotechnologies and biotechnological innovation can flourish.
This year Building the Bioeconomy has grown from thirteen economies to sixteen, adding Colombia, Israel and Japan. As in previous editions the sample of economies is geographically and economically diverse with a mix of high-income mature OECD economies and middle income and emerging markets.
Last year a key new feature of Building the Bioeconomy was the Biotech Policy Performance Measure. This tool (the ‘Measure’) provided readers a quick overview of a given economy’s policy framework and performance in relation to the other economies sampled. The Measure assessed the existence and performance of some of the most important elements for each of the seven enabling factors used to map a given economy’s biotechnology policy framework. This year the Biotech Policy Performance Measure has been expanded to now also take into account biotech outputs. Indicators on biotechnology outputs cover a broad spectrum ranging from levels of total clinical trial activity, clinical trials for biologics, scientific output, biotechnology crops under cultivation, venture capital attractiveness, biotechnology patenting, rates of university patenting, to biopharmaceutical product launches
Separating Fact from Fiction
How Localization Barriers Fail Where Positive Non-discriminatory Incentives Succeed
More in number and more draconian – Localization barriers have grown in number and intensity over the last decade. Our new study – Separating Fact from Fiction: How Localization Barriers Fail Where Positive Non-discriminatory Incentives Succeed – finds that over the last 5-10 years industrial aspirations and concern over their dependence on global supply chains have led many emerging markets to seek to bolster or create indigenous sectors through introducing protectionist-like measures.
However, the study also finds that restrictive and punitive conditioning localization barriers do not have the desired positive impact on economic activity or innovation. Looking for example at the levels of clinical research (a good proxy of high-level and sustained biopharmaceutical investment), the study finds that countries that have erected localization barriers – while exhibiting some of the strongest biopharmaceutical market growth rates and significant market size and potential – experience extremely low levels of clinical trials intensity. These negative results stand in stark contrast to the success of markets that focus on creating an enabling environment through positive non-discriminatory incentives and policies.
Additionally, building on the data and case studies the study sums up the negative impact localization barriers have through six ‘Myths and Facts’ with country specific examples. Covering some of the most common assumptions about the beneficial impact localization requirements can have, such as on domestic manufacturing / R&D capacity, access to innovative medicines, healthcare savings and effects on imports, the study provides a set of facts which show how these assumptions are not borne out by empirical evidence and international experience.
The Next Frontier in Ensuring the Quality of Medicines
Maintaining International Quality and Safety Standards in the Manufacturing and Supply of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Authored by Professor Meir Pugatch, Dr. David Torstensson and Ma’ayan Laufer this report provides a deep-dive analysis of the next generation of challenges facing drug regulators across the globe.
Pharmacovigilance is the name given to the mechanisms and tests that together map and ensure the safety of a medicine throughout its life span – from test tube to patient. As biopharmaceutical products are now manufactured and assembled through a complex global assembly line with numerous different suppliers, drug regulators are becoming cognizant of a new reality: ensuring high standards of quality is not just about monitoring and testing the safety of a finished product but also screening and monitoring the safety and quality of its key ingredients wherever in the world they are sourced and/or manufactured.
Overall the report finds that the API manufacturing and pharmacovigilance environment in the two largest producing countries, China and India, is currently lacking with regards to both the presence of adequate GMP and pharmacovigilance regulations as well as their enforcement. Analysis of both FDA and EMA warning letters show significant problems relating to quality control and integrity of API manufacturing in India and China. This is particularly worrying as foreign inspection rates by the FDA and EMA are far behind equivalent inspection rates within the US and EU. In practical terms it means that drug regulators in purchasing markets must now actively inspect and have a presence outside their respective legal jurisdictions.
Quantifying the Economic Gains of Strengthening India’s Clinical Research Policy Environment
Study and Key Findings
Coming from a relatively low starting point in its current level of clinical trial activity, India is a country that could benefit significantly from greater clinical trial activity. Why does such a gap exist between India’s potential in clinical trial activity and actual current levels? And how exactly might India benefit from addressing the factors behind this gap?
Pugatch Consilium releases Quantifying the Economic Gains of Strengthening India’s Clinical Research Policy Environment. The study analyzes India’s clinical research policy environment in relation to international best practices. Based on this analysis, it identifies which policy improvements might support greater clinical trial activity in the country and quantifies the wider, positive economic effects that could result under various scenarios of policy reform.
Overall the study finds that by addressing the most urgent policy elements within the area of clinical research – such as ambiguous definitions, procedures and protocols governing clinical research within the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, inadequate resources for needed capacity building, funding and infrastructure and lacking legal/IP environment – India stands to increase its number of new clinical trials per year from around 170 to above 800 and add over 600 million dollars in direct monetary transfers and indirect economic gains.
Building the Bioeconomy 2015
Examining National Biotechnology Industry Development Strategies Globally
The second edition study of the policies and best practices that pave the way for a creating an environment and ecosystem that enables biotech innovation. The 2015 edition focuses on 13 countries: Brazil, China, India, Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, Russia, Singapore, South Africa, Switzerland, Turkey, the UK and the United States. Using a comparative perspective and looking in detail at the country specific-level, the report identifies several important findings as well as lessons learned.
The report identifies seven enabling factors ranging from human capital, to R&D infrastructure to the protection of intellectual property rights that create the policy infrastructure upon which different countries can develop and promote their biotech ecosystems.
In addition to an expansion of the country sample, this year’s edition introduced a more focused sector specific analysis looking at the three main biotech sectors: biopharmaceuticals; ag-bio; and industrial biotechnology. While all the enabling factors are relevant for the different sectors of biotechnology, each sector also has different, specific policy needs.
This edition of Building the Bioeconomy also includes a new performance metric: a Biotech Policy Performance Measure. The purpose of this tool is to give readers (and the economies sampled) an idea of how a sample of their policies (including inputs and outputs) for each enabling factor compares with the same policy input or output for the other economies sampled.
BCI (Biopharmaceutical Competitiveness & Investment) 2015
Policy Environment Has a Significant Impact on Biopharmaceutical Investment
The BCI polls local managing directors and high level executives of multinational biopharmaceutical companies in 16 economies as to how different aspects of the local policy environment impact their ability to allocate investments to these markets. By gauging the on-the-ground “pulse” of a given market and translating it into a quantitative score, the BCI enables a unique and highly relevant snapshot of economies’ biomedical competitiveness.
The Evolution of Pharmacovigilance
Labeling, Packaging and Pharmacopeia Standards
This report provides a deep-dive analysis of the next generation of challenges facing pharmacoviglance regulators.
Pharmacovigilance is the name given to the mechanisms and tests that together map and ensure the safety of a medicine throughout its life span – from test tube to patient. As patients and healthcare professionals around the world access and use more biopharmaceutical products and technologies, the importance of maintaining and, in many cases, introducing and applying comprehensive pharmacovigilance regulations only increases.
Clinical Data and Disclosure Policies
The European Union, Member States, and International Best Practices
Pugatch Consilium, in partnership with the US Chamber’s Global Intellectual Property Center, releases Clinical Data and Disclosure Policies: The European Union, Member States, and International Best Practices. This report provides an exhaustive analysis of the clinical data transparency aspects of EU Parliament Regulation 536/2014 on clinical trials and EMA’s finalized policies on Publication and Access to Clinical Trials Data, as well as a review of the wider policy implications and interface of these policies vis-á-vis current data disclosure policies at five EU countries: Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, and the U.K.
How to stay one step ahead of an outbreak
Intellectual Property
Pugatch Consilium’s Prof. Meir Pugatch and Rachel Chu publish an article in fDi Magazine (http://www.fdiintelligence.com) on how building an innovation culture can help countries prepare for the outbreak of diseases such as Ebola. The article is part of Pugatch Consilium’s ongoing analysis and intelligence database on biopharmaceutical investment and innovation policy.
Unlimited Potential
GIPC International IP Index
Pugatch Consilium, in partnership with the US Chamber’s Global Intellectual Property Center, released the third edition of the annual GIPC International IP Index. The 2015 edition of the Index, entitled UP: Unlimited Potential, maps the intellectual property environment in 30 economies. Overall, although challenges remain across the board, positive steps are being taken in many of the economies included in the Index. In fact, 20 of the economies mapped in 2014 improved their scores in the 2015 edition. The report also underscores the benefits experience by countries as they strengthen their IP environments in a special section that correlates the GIPC Index scores with 15 variables reflecting key economic activities.
Developing a Culture of Pharmacovigilance
New Report On the Monitoring of Safety of Medicines
Pharmacovigilance is the name given to the mechanisms and tests that together map and ensure the safety of a medicine throughout its life span – from test tube to patient. As patients and healthcare professionals around the world access and use more biopharmaceutical products and technologies, the importance of maintaining and, in many cases, introducing and applying comprehensive pharmacovigilance regulations only increases.
Scaling Up Global Clinical Trial Activity
Key Trends and Policy Lessons
This report explains and quantifies key factors for attracting investment in clinical research. The report also benchmarks performance in the level and scope of clinical trial activity, providing a “who’s who” in global clinical research among countries and biopharmaceutical companies.
Pugatch Consilium’s latest study uses regression analysis of data on 50 countries to provide a roadmap for creating a policy environment that is conducive to clinical trials – a fundamental component of making safe and effective medicines available.
An excerpt of the study is available for download. To request a full copy of the study please email: info@pugatch-consilium.com
The Creative Industries and the BRICS
A review of the state of the creative economy in Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa
This review examines the state of the creative economy in the biggest emerging economies in the world namely Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa – the BRICS. Although at different levels of development, these economies are in many ways undergoing similar transitions from economies based on manufacturing, industrial output and natural resources to economies in which economic activity is based on innovation and creativity.
Building the Bioeconomy
Examining National Biotechnology Industry Development Strategies
This paper provides an overview of national innovation strategies, policies and best practices that relate to the building of a world-class biotechnology sector. It identifies key enabling policy input factors ranging from human capital, protection of intellectual property to infrastructure for research and development.
The Value of Cross-Border Data
The Value of Cross-Border Data to Consumers, Companies and Governments
The report considers the value and applications of cross-border data in different countries around the world today. It analyzes a wide range of personal, social and economic benefits using case studies and anecdotes as well as statistical analysis. The report also presents a set of enabling and deterrent factors of these flows.
Innovative Futures
A Scenario Analysis of Pharmaceutical Innovation and Access to Medicines in Europe
What does the process of creating these scenarios tell us about the approach that the pharmaceutical industry might choose to take to its interactions with policymakers both now and into the future?
Considering two distinct scenarios – “Suspicious Minds” and “Convergence” – this report explores the possible evolution of pharmaceutical innovation, access and financing of medicines in Europe, over a period of 10 years.
GIPC Index
The GIPC Index highlights both improvements and impediments to creating robust IP environments.
In the 21st century, nations continue to look for the best policies to promote innovation, create jobs, and attract investment. The second edition of the GIPC Index provides an academically-rigorous guide for all countries to improve their IP environment and help chart a course to prosperity.
Direct link to the report can also be found on the GIPC Website (U.S. Chamber of Commerce).
Clinical Trials and Data Transparency
The Public Interest Case
Objective: The public and scientific community obtain increased access to enhance knowledge about medical advancements and regulatory accountability without compromising personal privacy or long-term incentives for biopharmaceutical R&D.
Scope: Personal data and CCI receive special treatment; all other data submitted to the EMA following the introduction of the draft policy will be proactively published.
Scientific American – World View: Does Your Country Deserve Investment From Biopharma?
An ongoing survey of executives and a resulting country index will reveal who is ready to compete for capital.
The BCI (Biopharmaceutical Competitiveness & Investment) is a global survey-based instrument translated to quantifiable index with a Bottom-up approach: relies on the expertise and experience of local executives; provides “On the ground” perspective of countries’ attractiveness to biopharmaceutical investment and enhances understanding of where national improvements are needed.
Biopharmaceutical Competitiveness & Investment (BCI) Survey
How attractive is your country for investment? Ask the experts
The BCI is a global survey-based instrument translated to quantifiable index with a Bottom-up approach: relies on the expertise and experience of local executives; provides “On the ground” perspective of countries’ attractiveness to biopharmaceutical investment and enhances understanding of where national improvements are needed.
Assembling the Pharmaceutical R&D Puzzle for Needs in the Developing World
An assessment of new and proposed delinking initiatives aimed at encouraging R&D into neglected and tropical diseases and specific Type II diseases.
London Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases
What does the “London Declaration on Neglected Tropical Diseases” reveal about research and development efforts into neglected and tropical diseases?
Gates Foundation, USAID, DfID, the WHO, DNDi, the Governments of Mozambique, Tanzania, Brazil and a host of multinational biopharmaceutical manufacturers including GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Eisai, Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, Novartis, Bayer and Abbott, committed to eradicate and control a number of neglected and tropical diseases (NTDs).
This brief will examine the declaration, the pledges made and the methods to be used.
ACTA protesters – Do They Have the Wrong Target?
The week of February 6, 2012 saw fresh opposition to the ACTA treaty across Europe, including an online petition which received over 2,000,000 signatures and more than 100 protests in major cities on Saturday, February 11.2 Protesters are calling for the European Parliament to reject the treaty, which they say restricts fundamental rights. Although the European Union and 22 member states have already signed on to ACTA last month, it still needs to be ratified by the European Parliament and implemented by member states.
R&D Tax Credits – Economic Rationale and Impact
The use of R&D tax credits is a growing area of interest for governments and policymakers around the world seeking to stimulate economic activity and innovation. What is the economic rationale behind the R&D tax credit? What do current tax credits look like within the OECD and G20? And do these tax credits stimulate and attract more R&D investment?
Growing the global solar sector – Will investors take a short-term or holistic perspective?
Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) released figures showing that overall global investment in clean energy reached record highs in 2011, with investment in solar technologies by far the highest. Yet at the same time, 2011 saw a drop in spending on clean energy R&D, and further reductions are expected. Given the increasing dominance of the solar sector, what does this mean for countries, particularly emerging economies, seeking to incorporate solar and other clean energy sources into their energy supplies?
Taking Stock – the Launch of Google Music and the State of Online Copyright Protection
Does the launch of Google Music mark a significant departure in the effort to create a digital platform that can compete with pirated media? Moreover, can it finally bring the music industry back to revenue levels of the early 2000s?
On November 11 Google launched the latest of its initiatives to broaden its brand into new territory. The search-engine behemoth is a major technology player with a vast array of cloud and device-based services ranging from mobile software (Android) to email, office software services, and now music.
On numbers and Access to Medicines – CBO Figures on the PAAG Act are not that Convincing
Will the proposed Preserve Access to Affordable Generics (PAAG) Act actually generate the $4.8 billion savings over 10 years that the Congressional Budget Office suggests it will? How realistic are its assumptions about generic competition or healthcare costs over the next ten years?
The Preserve Access to Affordable Generics Act (S.27), introduced in October 2011, would make illegal patent settlement agreements which pay generic companies a fee to settle drug patent litigation in return for agreeing to withhold marketing their generic drugs until the end, or shortly before, the expiration of the patent under dispute.
Survey of Licensing Activities in Selected Fields of Environmentally Sound Technologies (ESTs)
A Joint Project by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the European Patent Office (EPO), and the International Centre for Trade and Sustainable Development (ICTSD)
This survey was distributed among leading organizations that are active in the development, patenting, commercialization and transfer of ESTs. More than 160 organizations answered the survey, including companies from the private sector, academic institutions, governmental bodies, national research laboratories, consortiums, etc.